Question 1 (a)

Question 1 (b)
How to interpret the z-score
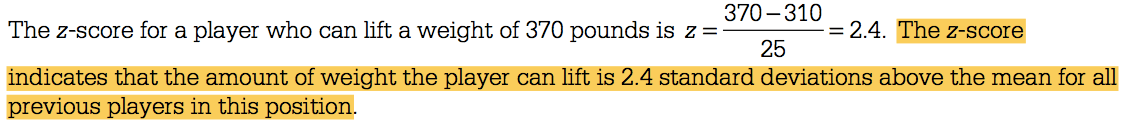
Question 2 (b)
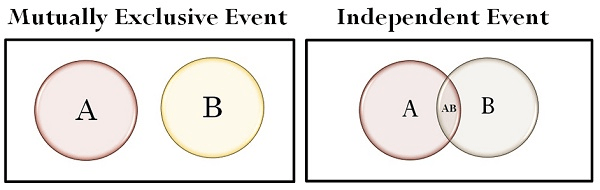
Independence vs. Dependence
A conditional probability is the probability of some event occurring, given that some other event has already occurred. The conditional probability of event X occurring, given that some other event Y has already occurred, is written as P(X|Y).
For example, P(M|N) would be the probability of the occurrence of event M given that event N has already occurred. It would be read as “the probability of M, given N.”
As stated earlier, two events are considered independent if the occurrence of one of the events does not change the probability of the other event from what it would have been had the first event not occurred. Thus, two events, X and Y, are independent if P(X|Y) = P(X) or P(Y|X) = P(Y)
Actually, these two conditional relationships are related. If one is true, the other must be true. If one is false, the other must be false.
If P(X|Y) = P(X), then P(Y|X) = P(Y), and the events are independent.
If P(X|Y) ≠ P(X), then P(Y|X) ≠ P(Y), and the events are dependent.
Question 2 (c)

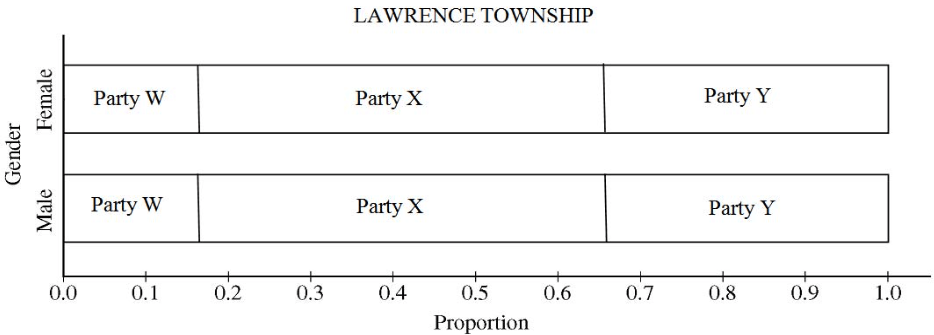
Question 3 (a)
Process for randomly selecting 2 numbers from 1 to 9

Question 3 (b)

Question 4
Degrees of freedom for two-sample t-test.
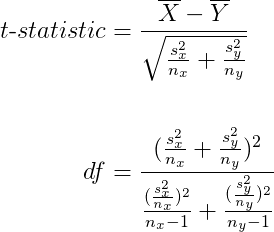
Graphs of both distributions must be produced and described to check the normality condition.
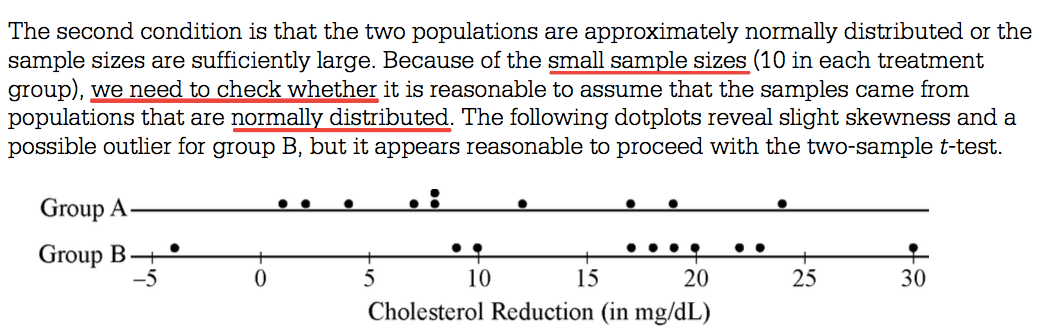
Question 5 (c)
Correlation coefficient
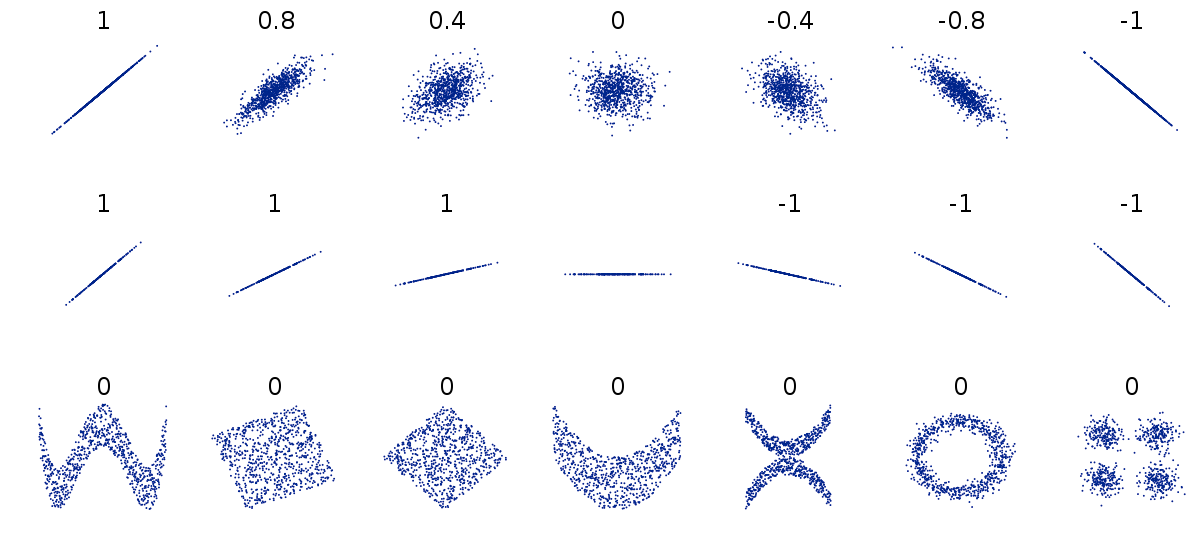
Coefficient of determination

Question 5 (d)
Explaining relationship

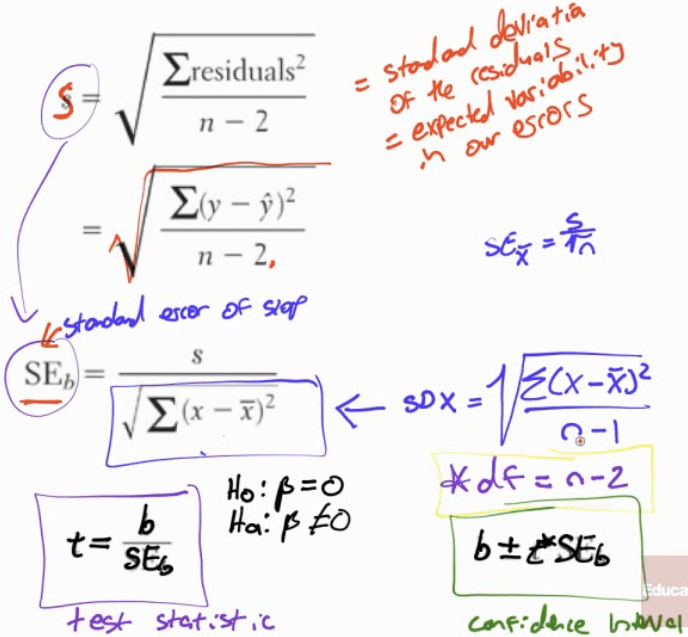
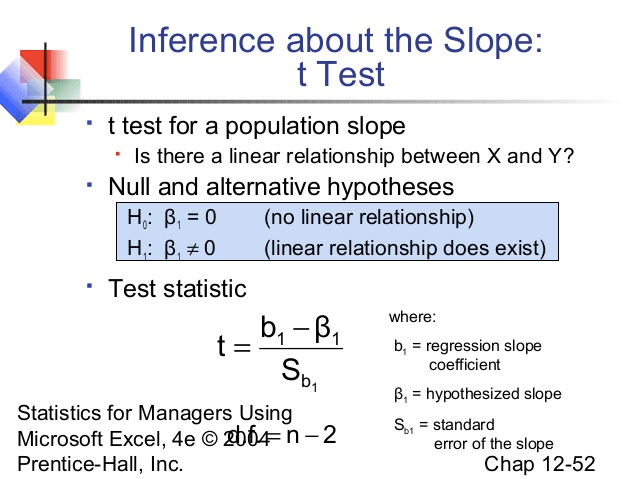
Question 6 (a)
Checking condition for one-sample z-interval
Random
Normal: Large sample size
